GENERAL
Fibromyalgia is a chronic painful disease, from which about 5 million people suffer only in the U.S.A. Patients feel tenderness, pain and rigidity of muscles and ligaments, without any notable findings in X-rays and other laboratory examinations.
Fibromyalgia does not afflict joints and internal organs, but the permanent pain and feeling of fatigue induced have a dramatic effect on the life quality of patients and their families.
Fibromyalgia is often accompanied with fatigue, poor sleep, anxiety, depression and intestinal disorders.
The aetiology of the disease is unknown. The painful sites are not accompanied with tissue inflammation. Therefore, patients with fibromyalgia do not have any physical defect or deformity.
Fibromyalgia is different from other rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis and systematic lupus erythematosus. In contrast to fibromyalgia, in these diseases the pain is due to tissue inflammation. Also, there may be impairment and deformity of joints and other internal organs.
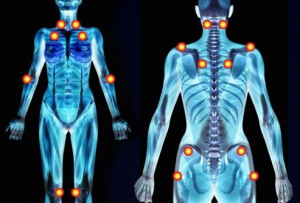
There are 18 tender points in the body, which have been specified by physicians. When pressure is exerted on these points, pain is induced. This type of handling is part of the diagnostic testing for fibromyalgia.
The painful points are located symmetrically to the anterior and posterior surface of the body.
- Front lower sides of neck
- Back of the head
- Front upper chest
- Back upper chest
- Top of shoulders
- Inner side of elbows
- Upper outer side of buttocks
- Sides of hip joints
- Inner sides of knees
The painful points have the size of the head of a pin. They are located around the joints, but the fibromyalgia itself has no relation with arthritic pain.
The most characteristic symptom of fibromyalgia is the chronic diffuse muscle pain.
The diagnosis is set by provoking pain to at least 11 out of the 18 trigger points of the body (described above in the paragraph “Anatomy of Fibromyalgia”).
Unlike the pain of the myoperitoneal syndrome, the fibromyalgia pain is not limited only locally at the painful points but is diffuse, intense and described by patients as “a feeling of pressure, pinching and burning sensation”. Muscles may be hard and stiff.
Patients with fibromyalgia feel permanent fatigue, regardless of their physical activity, and they characteristically wake up in the morning equally tired as before going to bed at night.
The range of motion of their joints is often limited and for this reason the disease is frequently confused with rheumatoid arthritis.
The quality of sleep is poor and certain sleep measurements have shown that their brain presents periodical intense activity in deep sleep levels. As a result, their organism neither rests nor recovers sufficiently during sleep.
Patients with fibromyalgia often present with anxiety and depression, resulting in social isolation and dramatic decline of their life quality.
Other less common symptoms in fibromyalgia are:
- Morning stiffness
- Pain following exercise
- Poor concentration
- Confusion
- Dysmenorrhoea (painful menstruation)
- Sensitivity to contact, light and noise
Diseases that may coexist with fibromyalgia and have to be differentially diagnosed are:
- Migraine
- Temporomandibular joint disorder
- Restless leg syndrome
- Raynaud Syndrome
- Irritable bowel (abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea or constipation or both alternately)
- Irritable bladder (high frequency of urination)
The American Food and Drug Association (FDA) have officially approved three drugs for the treatment of fibromyalgia:
- Pregabalin (Lyrica)
- Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
- Milnacipran (Savella)
However, many other drugs are administered for the treatment of concomitant symptoms in fibromyalgia.
- ANTIEPILEPTIC DRUGS
Pregabalin is an antiepileptic drug indicated also for the treatment of the neuropathic pain and is one of the three drugs officially approved by FDA for the treatment of fibromyalgia.
Another antiepileptic drug administered for the treatment of concomitant disorders and symptoms in fibromyalgia is Gabapentin (Neurontin).
- ANTIDEPRESSANTS
1.Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitryptyline (Saroten) and Nortriptyline. These drugs are administered for improving mood, pain and quality of sleep.
2. Serotonine & Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs). The drugs of this category increase the levels of neurotransmitters serotonine and noradrenaline in brain cells, affecting positively the mood and reducing pain. Such drugs are Duloxetine (Cymbalta) and Milnacipran (Savella).
3.Selective Serotonine Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs). They selectively increase Serotonine levels in the organism, improving mainly the mood and quality of sleep.
- MUSCLE RELAXANTS
Muscle relaxants are administered to reduce the stiffness and rigidity of muscles. They may contribute to improving the quality of sleep and reducing pain of the temporomandibular joint.
OTHER ADJUVANT DRUGS
- NON STEROID ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS & PARACETAMOLE
These drugs on their own are not indicated for the treatment of fibromyalgia pain, for, as already mentioned, there is no inflammation. However, they may help in treating some concomitant symptoms and disorders, such as migraine, dysmenorrhoea etc.
- BENZODIAZEPINES
Drugs of this category (such as Stedon, Valium, Xanax etc) relax muscles and improve the quality of sleep. These are drugs which may cause addiction and have to be prescribed only after the judgment and close follow-up by the therapist physician.
- MILD OPIOIDS
Tramadole and Codeine are drugs administered to control pain in case the previous drugs or their combination do not provide satisfactory analgesia. They do not have as severe potential side effects as strong opioids. Their efficacy in fibromyalgia is in doubt.
- ACUPUNCTURE
This is an ancient therapeutic method, still used today after having undergone many modifications and improvements throughout centuries. Its roots originate from ancient China. Acupunture is based on the observation that a highly significant role in the function of the human body is played by some energy paths involving basic nerves or groups of neurons, which in acupuncture are called “meridians”. Along the course of these meridians, there are some points to which we intervene with mechanical stimulation (in acupuncture by inserting needles in the skin in different depths accordingly) and improve the distorted flow of energy producing a therapeutic result.
According to the patient’s symptoms, the Acupuncturist inserts several very fine needles on various specific points of the body, which have to stay there for 20-40 minutes.
According to another consideration, acupuncture stimulates the release of endorphins in the blood flow by the body organism itself. Endorphins are natural analgesic substances of the organism which reduce the intensity of pain in a natural way without side effects.
A modified form of classical acupuncture is Electro-acupuncture. In Electro-acupuncture, the needles have a wire connected to an electric source that generates and transfers electric pulses stimulating the points where the needles are inserted.
- MASSAGE
Although it is not proven that massage alleviates pain in fibromyalgia, it is believed that it generally has a beneficial effect contributing to muscle relaxation and improvement of stiffness.
There are various types of massage, such as swedish massage, sports massage, relaxation massage etc.
- ANTI-ANXIETY THERAPIES
These are applied by Psychiatrists and Psychologists and are not pharmaceutical therapies.
WHICH MEDICAL SPECIALTIES ARE INVOLVED IN THE TREATMENT OF FIBROMYALGIA
- RHEUMATOLOGISTS
Rheumatologists are physicians specialized in the diagnosis and treatment of arthritis and diseases of muscle joints and soft tissues. They follow the developments in fibromyalgia and probably have the best knowledge for its treament. However, this is not true for all Rheumatologists.
- NEUROLOGISTS
Neurologists deal with the treatment of diseases of the nervous system and the brain. Many Neurologists know fibromyalgia, but, as it happens with Rheumatologists, not all of them are familiar with the treatment of this specific disease. The patients who visit a Neurologist for the treatment of fibromyalgia pain, receive pharmaceutical treatment with neurological drugs.
- PAIN PHYSICIANS (ALGOLOGISTS)
Pain Physicians are well aware of how to treat any kind of chronic pain. However, before visiting a Pain Clinic, you should ask for one dealing more specifically with fibromyalgia, for there are Pain Physicians who do not deal with this specific disease.
Αρχή φόρμας
Τέλος φόρμας